2 What are the different types of errors in PHP?
3 What is the difference between mysql_fetch_object and mysql_fetch_array?
5 How many ways I can register the variables into session?
13: What are Abstract Classes and Methods?
17: Abstract Class vs Interface
1.
what is GETTER and SETTER?
“Getters” and “Setters” are object methods that allow you to control access to a certain class variables / properties. ... A “getter” allows to you to retrieve or “get” a given property. A “setter” allows you to “set” the value of a given property.
2
What are the different types of Errors in PHP?
There are three basic types of runtime errors in PHP:
1. Notices: These are small, non-critical errors that PHP encounters while executing a script - for example, accessing a variable that has not yet been defined. By default, such errors are not displayed to the user at all - although the default behavior can be changed.
2. Warnings: Warnings are more severe errors like attempting to include() a file which does not exist. By default, these errors are displayed to the user, but they do not result in script termination.
3. Fatal errors: These are critical errors - for example, instantiating an object of a non-existent class, or calling a non-existent function. These errors cause the immediate termination of the script, and PHP's default behavior is to display them to the user when they take place.
- E_ERROR: A fatal error that causes script termination
- E_WARNING: Run-time warning that does not cause script termination
- E_PARSE: Compile time parse error.
- E_NOTICE: Run time notice caused due to error in code
- E_CORE_ERROR: Fatal errors that occur during PHP's initial startup (installation)
- E_CORE_WARNING: Warnings that occur during PHP's initial startup
- E_COMPILE_ERROR: Fatal compile-time errors indication problem with script.
- E_USER_ERROR: User-generated error message.
- E_USER_WARNING: User-generated warning message.
- E_USER_NOTICE: User-generated notice message.
- .E_STRICT: Run-time notices.
- E_RECOVERABLE_ERROR: Catchable fatal error indicating a dangerous error
- E_ALL: Catches all errors and warnings
3 Mysql_fetch_object returns the result from the database as objects while mysql_fetch_array returns result as an array. This will allow access to the data by the field names. E.g. using mysql_fetch_object field can be accessed as $result->name and using mysql_fetch_array field can be accessed as $result->[name]
4
- Avoid the use of global variables. Hence it must be ensured that register_globals option is not enabled.
- Use of variables designed to be set by GET or POST requests.
- Store passwords in an encrypted format
- Avoid storing credit card and other secured information. Trust a third party gateway.
- Make use of server side validations and avoid trusting the user input.
Example: if the expected value is integer, use the intval function.
$post_id = intval($_GET['post_id']);
mysql_query("SELECT * FROM post WHERE id = $post_id"); - Avoid using user input directly in the query. Mysql_real_escape_string()
- Always use the updated version of php.
5
How many ways I can register the variables into session?
Session_register(“smple”);
$_session can also be used for registering variables.
$_SESSION['count'] = 0;
Removing session data
The session data can be removed using the unset() function. Only specific elements of the $_SESSION array should be unset.
<?php
$_SESSION[‘sample’]=1;
Print $_SESSION [‘sample’];
Unset ($_SESSION[‘sample’);
?>
Ending a session
A session lasts until the browser window is not closed. In order to explicitly end the session Session_destory(); is used for ending the session.
6 : What is ENCAPSULATION?
Answer: Encapsulation is an OOP (Object Oriented Programming) concept in PHP. Wrapping some data in single unit is called Encapsulation. ... Second advantage of encapsulation is you can make the class read only or write only by providing setter or getter method. Capsule is best example of Encapsulation.
class employee { public $name; private $id; protected $tax; public $age; }
If you have to access private/protected properties, you can use getter and setter methods in your class.
As the name states,
The getter method retrieves an attribute in other classes.
The setter method modifies/changes the value of the attribute/data..
7.
Design PATTERN
https://phptherightway.com/pages/Design-Patterns.html
Answer: singleton, factory,
Factory
One of the most commonly used design patterns is the factory pattern. In this pattern, a class simply creates the object you want to use.
Singleton
When designing web applications, it often makes sense conceptually and architecturally to allow access to one and only one instance of a particular class. The singleton pattern enables us to do this.
The code above implements the singleton pattern using a static variable and the static creation method getInstance(). Note the following:
The constructor __construct() is declared as protected to prevent creating a new instance outside of the class via the new operator.
The magic method __clone() is declared as private to prevent cloning of an instance of the class via the clone operator.
The magic method __wakeup() is declared as private to prevent unserializing of an instance of the class via the global function unserialize() .
A new instance is created via late static binding in the static creation method getInstance() with the keyword static. This allows the subclassing of the class Singleton in the example.
The singleton pattern is useful when we need to make sure we only have a single instance of a class for the entire request lifecycle in a web application.
Strategy
Model-View-Controller commonly used in PHP frameworks like CI,Cake,Laravel
With the strategy pattern you encapsulate specific families of algorithms allowing the client class responsible for instantiating a particular algorithm to have no knowledge of the actual implementation.
This first code snippet outlines a family of algorithms; you may want a serialized array, some JSON or maybe just an array of data:
<?php
interface OutputInterface
{
public function load();
}
class SerializedArrayOutput implements OutputInterface
{
public function load()
{
return serialize($arrayOfData);
}
}
class JsonStringOutput implements OutputInterface
{
public function load()
{
return json_encode($arrayOfData);
}
}
class ArrayOutput implements OutputInterface
{
public function load()
{
return $arrayOfData;
}
}
.
8
Treat
Answer: Traits are a mechanism for code reuse in single inheritance languages such as PHP.
Traits are used to declare methods that can be used in multiple classes.
So, what if a class needs to inherit multiple behaviors
PHP only supports single inheritance: a child class can inherit only from one single parent.
So, what if a class needs to inherit multiple behaviors? OOP traits solve this problem.
Traits can have methods and abstract methods that can be used in multiple classes, and the methods can have any access modifier (public, private, or protected).
Traits are declared with the trait keyword:
<?php
trait TraitName {
// some code...
}
?>
<?php
class MyClass {
use TraitName;
}
?>
<?php
trait message1 {
public function msg1() {
echo "OOP is fun! ";
}
}
class Welcome {
use message1;
}
$obj = new Welcome();
$obj->msg1();
?>
<?php
trait message1 {
public function msg1() {
echo "OOP is fun! ";
}
}
trait message2 {
public function msg2() {
echo "OOP reduces code duplication!";
}
}
class Welcome {
use message1;
}
class Welcome2 {
use message1, message2;
}
$obj = new Welcome();
$obj->msg1();
echo "<br>";
$obj2 = new Welcome2();
$obj2->msg1();
$obj2->msg2();
?>
9 What is POLYMORPHISM
POLYMORPHISM
Answer: But PHP "does not support" compile time polymorphism, which means function overloading and operator overloading
Question6: Does php support OVERLOADING
OVERLOADING
Answer: Actually PHP does support function overloading, but in a different way. ... PHP's interpretation of "overloading" is different than most object oriented languages. Overloading traditionally provides the ability to have multiple methods with the same name but different quantities and types of arguments.
dynamically "create" properties and methods using of MAGIC method. ex: func_get_args(), gettype()..
10. what is MAGIC
MAGIC
method
Answer: some special functions that will be called automatically.
11. what is Constants
Constants
class
Answer:
Constants cannot be changed once it is declared.
Class constants can be useful if you need to define some constant data within a class.
A class constant is declared inside a class with the const keyword.
Class constants are case-sensitive. However, it is recommended to name the constants in all uppercase letters.
We can access a constant from outside the class by using the class name followed by the scope resolution operator (::) followed by the constant name, like here:
<?php
class Goodbye {
const LEAVING_MESSAGE = "Thank you for visiting W3Schools.com!";
}
echo Goodbye::LEAVING_MESSAGE;
?>
12.
Static Methods
Answer:
Static methods can be called directly - without creating an instance of a class.
Static methods are declared with the static keyword:
<?php
class ClassName {
public static function staticMethod() {
echo "Hello World!";
}
}
?>
ClassName::staticMethod();
13. What are Abstract Classes and Methods?
Abstract Classes
Answer:
Abstract classes and methods are when the parent class has a named method, but need its child class(es) to fill out the tasks.
An abstract class is a class that contains at least one abstract method. An abstract method is a method that is declared, but not implemented in the code.
<?php
abstract class ParentClass {
abstract public function someMethod1();
abstract public function someMethod2($name, $color);
abstract public function someMethod3() : string;
}
?>
14.
Namespaces
Answer:
They allow the same name to be used for more than one class
15.
Inheritance
Answer:
Inheritance in OOP = When a class derives from another class.
The child class will inherit all the public and protected properties and methods from the parent class. In addition, it can have its own properties and methods.
An inherited class is defined by using the extends keyword.
?php
class Fruit {
public $name;
public $color;
public function __construct($name, $color) {
$this->name = $name;
$this->color = $color;
}
public function intro() {
echo "The fruit is {$this->name} and the color is {$this->color}.";
}
}
// Strawberry is inherited from Fruit
class Strawberry extends Fruit {
public function message() {
echo "Am I a fruit or a berry? ";
}
}
$strawberry = new Strawberry("Strawberry", "red");
$strawberry->message();
$strawberry->intro();
?>
16.
Access Modifiers
Answer:
public, protected, private
17.
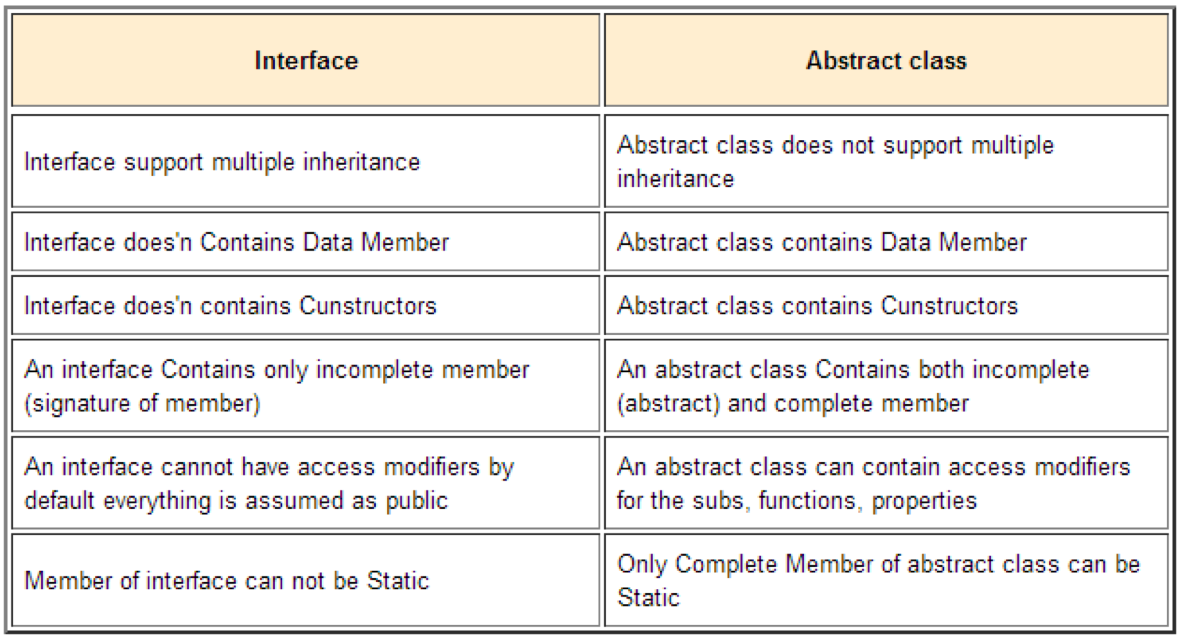
Abstract Class vs Interface
Answer:
interface Interface_A { } interface Interface_B { } interface Interface_C { }
interface MyInterface extends Interface_A, Interface_B, Interface_C { }
18.
Share on FacebookPage views: 174991